UNIT2.2 LlamaIndex Frameworks¶
1. LlamaIndex简介¶
LlamaIndex是一个为构建LLM驱动智能体提供的完整工具包,主要通过索引和工作流处理您的数据。其核心组成包括:
- 组件:基础构建模块,如提示词、模型和数据库等
- 工具:提供特定功能的组件,用于搜索、计算或访问外部服务
- 智能体:能够自主使用工具并做出决策的独立组件
- 工作流:按步骤处理逻辑的流程,无需显式使用智能体即可构建智能行为
LlamaIndex的独特优势:
- 清晰的工作流系统:通过事件驱动和异步优先的语法逐步分解决策过程
- 高级文档解析:基于LlamaParse的专业文档解析工具
- 丰富的即用组件:与众多框架兼容,提供大量验证可靠的组件
- LlamaHub:包含数百个集成组件、智能体和工具的注册中心
2. LlamaHub简介¶
LlamaHub是一个包含数百个集成组件、智能体和工具的注册中心,为LlamaIndex框架提供资源。
1. 安装组件
安装命令遵循统一格式:
例如,安装Hugging Face推理API集成:
2. 使用示例
from llama_index.llms.huggingface_api import HuggingFaceInferenceAPI
llm = HuggingFaceInferenceAPI(
model_name="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct",
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=100,
token="hf_xxx",
)
llm.complete("Hello, how are you?")
# 输出: I am good, how can I help you today?
3. LlamaIndex中的组件¶
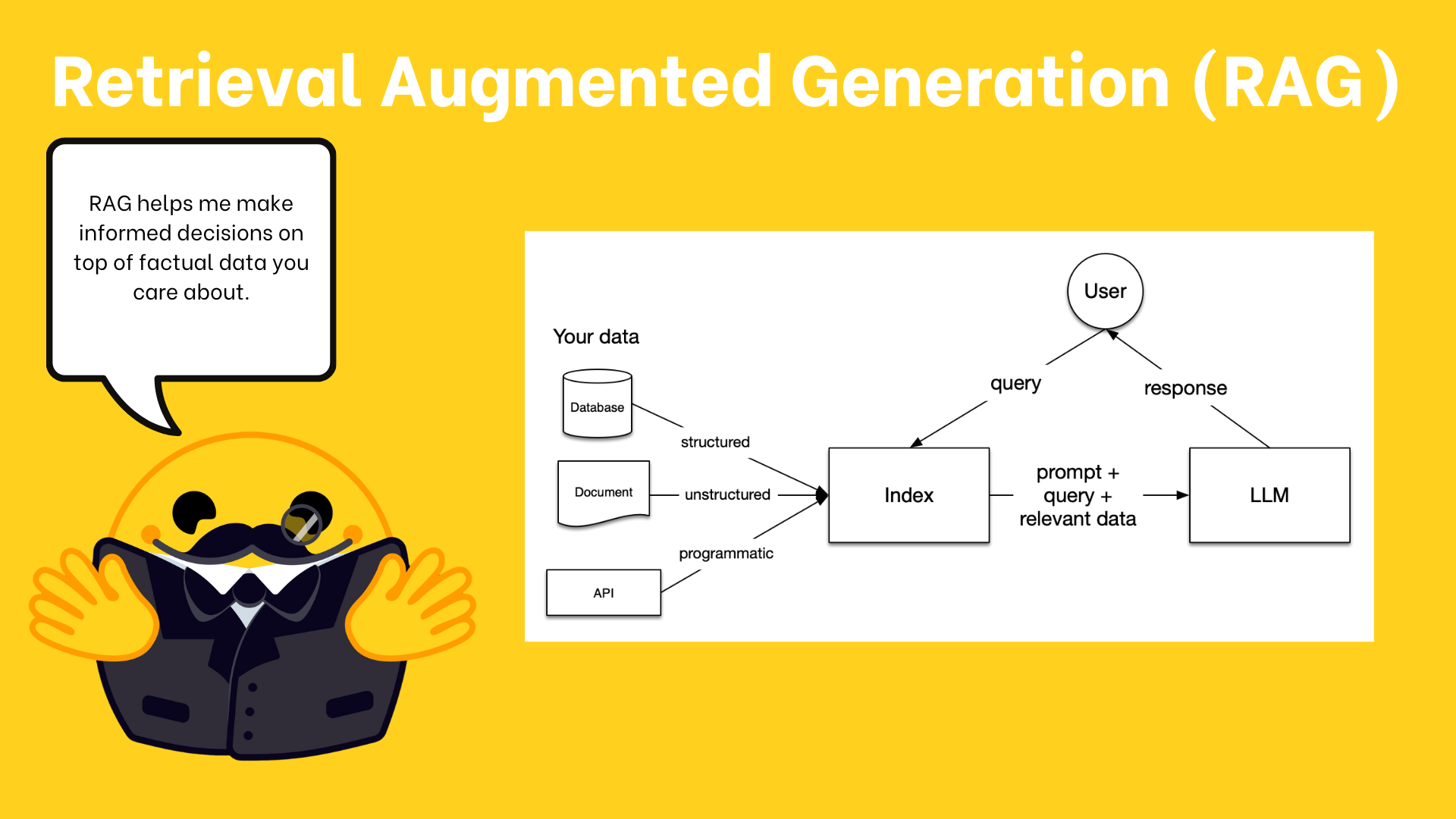
#RAG流程的五个关键阶段
- 加载:从原始位置导入数据
- 索引:创建便于查询的数据结构
- 存储:持久化存储索引,避免重复构建
- 查询:支持多种检索策略
- 评估:通过客观指标评估响应质量
#数据加载与嵌入
LlamaIndex提供三种主要数据加载方式:
- SimpleDirectoryReader:从本地目录加载多种文件类型
- LlamaParse:官方PDF解析工具
- LlamaHub:包含数百个数据加载库的注册中心
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
reader = SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="path/to/directory")
documents = reader.load_data()
加载后需要将文档分解为更小的Node对象:
from llama_index.core import Document
from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface_api import HuggingFaceInferenceAPIEmbedding
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.core.ingestion import IngestionPipeline
# 创建摄取管道
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[
SentenceSplitter(chunk_overlap=0),
HuggingFaceInferenceAPIEmbedding(model_name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5"),
]
)
nodes = await pipeline.arun(documents=[Document.example()])
#存储与索引文档
使用向量存储来存储文档:
import chromadb
from llama_index.vector_stores.chroma import ChromaVectorStore
db = chromadb.PersistentClient(path="./alfred_chroma_db")
chroma_collection = db.get_or_create_collection("alfred")
vector_store = ChromaVectorStore(chroma_collection=chroma_collection)
pipeline = IngestionPipeline(
transformations=[
SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=25, chunk_overlap=0),
HuggingFaceInferenceAPIEmbedding(model_name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5"),
],
vector_store=vector_store,
)
创建向量存储索引:
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface_api import HuggingFaceInferenceAPIEmbedding
embed_model = HuggingFaceInferenceAPIEmbedding(model_name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5")
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_vector_store(vector_store, embed_model=embed_model)
#查询VectorStoreIndex
查询索引的常见转换选项:
- as_retriever:基础文档检索
- as_query_engine:单次问答交互
- as_chat_engine:保持跨消息记忆的对话交互
from llama_index.llms.huggingface_api import HuggingFaceInferenceAPI
llm = HuggingFaceInferenceAPI(model_name="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct")
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(
llm=llm,
response_mode="tree_summarize",
)
query_engine.query("What is the meaning of life?")
# 输出: The meaning of life is 42
#响应处理
查询引擎使用ResponseSynthesizer作为响应处理策略,提供三种工作策略:
- refine(迭代优化):逐个处理每个检索到的文本块
- compact(紧凑模式,默认):预先拼接文本块,减少LLM调用次数
- tree_summarize(树状归纳):构建答案的树状结构生成详细响应
#评估与可观测性
LlamaIndex提供内置评估工具:
- FaithfulnessEvaluator:验证答案是否得到上下文支持
- AnswerRelevancyEvaluator:评估答案与问题的关联程度
- CorrectnessEvaluator:检验答案的正确性
from llama_index.core.evaluation import FaithfulnessEvaluator
evaluator = FaithfulnessEvaluator(llm=llm)
response = query_engine.query("What battles took place in New York City in the American Revolution?")
eval_result = evaluator.evaluate_response(response=response)
eval_result.passing
4. 在LlamaIndex中使用工具¶

LlamaIndex中主要包含四种工具类型:
- FunctionTool:将任意Python函数转换为智能体可用的工具
- QueryEngineTool:让智能体能够使用查询引擎
- Toolspecs:社区创建的预设工具集
- Utility Tools:处理大量数据的特殊工具
#创建FunctionTool
from llama_index.core.tools import FunctionTool
def get_weather(location: str) -> str:
"""Useful for getting the weather for a given location."""
print(f"Getting weather for {location}")
return f"The weather in {location} is sunny"
tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(
get_weather,
name="my_weather_tool",
description="Useful for getting the weather for a given location.",
)
tool.call("New York")
#创建QueryEngineTool
from llama_index.core.tools import QueryEngineTool
tool = QueryEngineTool.from_defaults(
query_engine,
name="some useful name",
description="some useful description"
)
#创建Toolspecs
Toolspecs是可以和谐协作的工具集合:
from llama_index.tools.google import GmailToolSpec
tool_spec = GmailToolSpec()
tool_spec_list = tool_spec.to_tool_list()
# 查看工具元数据
[(tool.metadata.name, tool.metadata.description) for tool in tool_spec_list]
#实用工具
有两种主要的实用工具:
- OnDemandToolLoader:将任何现有的LlamaIndex数据加载器转化为智能体可使用的工具
- LoadAndSearchToolSpec:接受任何现有工具作为输入的工具规范,返回加载工具和搜索工具
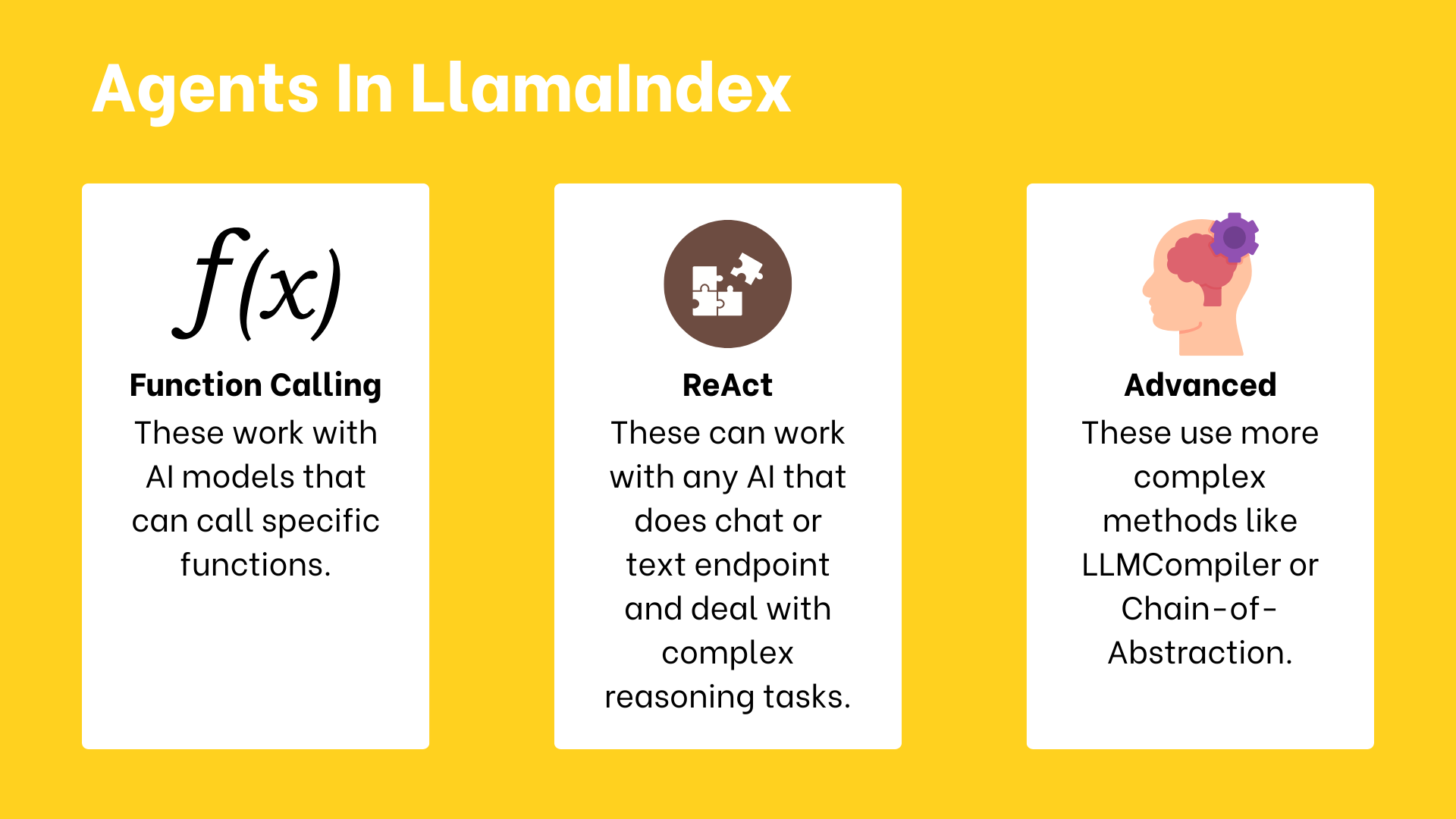
5. 在LlamaIndex中使用智能体¶
LlamaIndex支持三种主要类型的推理智能体:
- 函数调用智能体:适用于支持调用特定函数的AI模型
- ReAct智能体:适用于具有聊天或文本完成能力的AI模型,擅长复杂推理任务
- 高级自定义智能体:使用更复杂方法处理高阶任务和工作流
#初始化智能体
创建智能体需要为其提供定义能力的工具集合:
from llama_index.llms.huggingface_api import HuggingFaceInferenceAPI
from llama_index.core.agent.workflow import AgentWorkflow
from llama_index.core.tools import FunctionTool
# 定义示例工具
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiplies two integers and returns the resulting integer"""
return a * b
# 初始化LLM
llm = HuggingFaceInferenceAPI(model_name="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct")
# 初始化智能体
agent = AgentWorkflow.from_tools_or_functions(
[FunctionTool.from_defaults(multiply)],
llm=llm
)
智能体默认是无状态的,如需记忆过往交互,需显式使用Context对象:
# 无状态调用
response = await agent.run("What is 2 times 2?")
# 记忆状态
from llama_index.core.workflow import Context
ctx = Context(agent)
response = await agent.run("My name is Bob.", ctx=ctx)
response = await agent.run("What was my name again?", ctx=ctx)
#使用QueryEngineTools创建RAG智能体
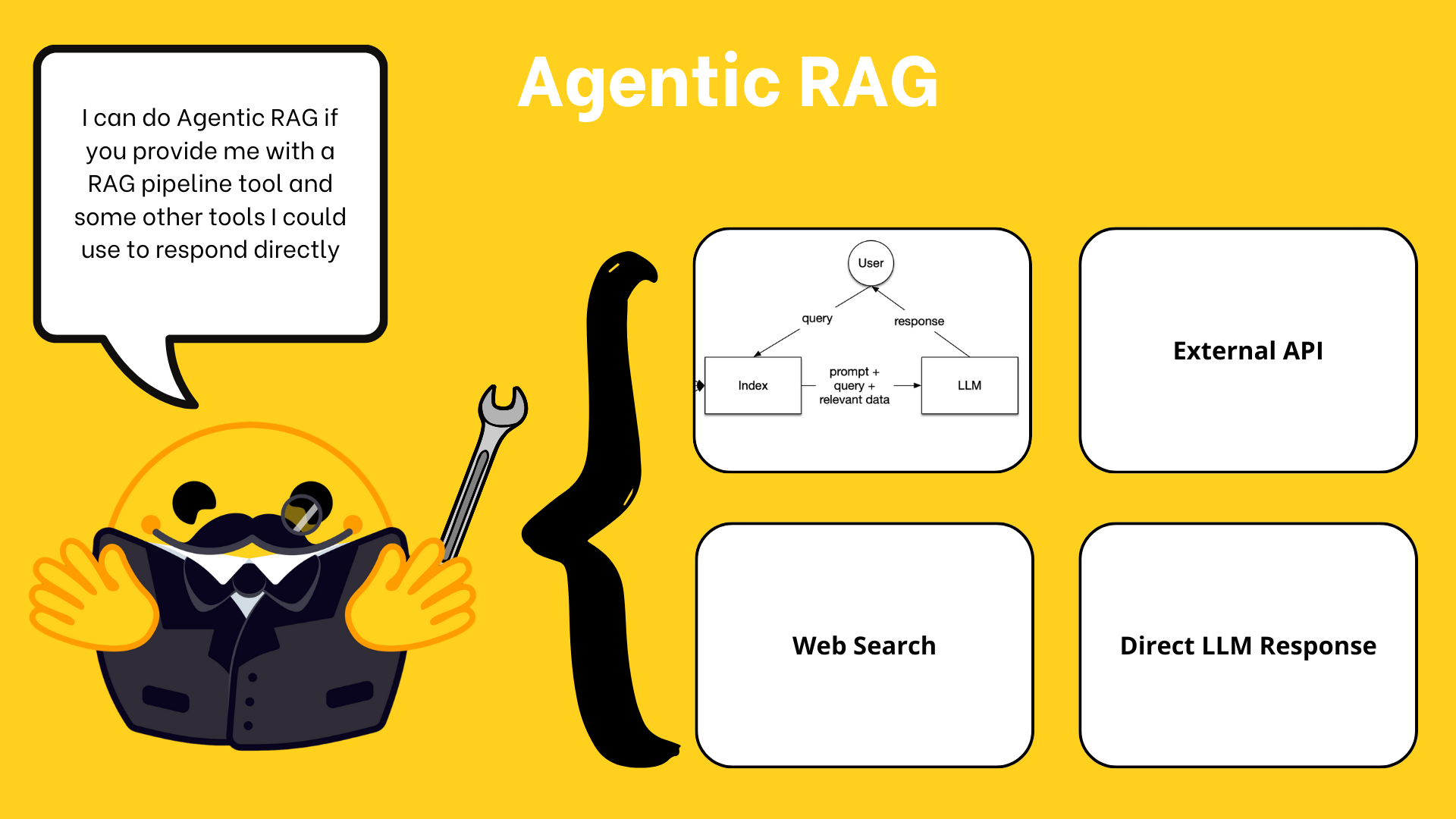
智能体增强检索(Agentic RAG)是通过智能体实现数据问答的强大范式:
from llama_index.core.tools import QueryEngineTool
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(llm=llm, similarity_top_k=3)
query_engine_tool = QueryEngineTool.from_defaults(
query_engine=query_engine,
name="name",
description="a specific description",
return_direct=False,
)
query_engine_agent = AgentWorkflow.from_tools_or_functions(
[query_engine_tool],
llm=llm,
system_prompt="You are a helpful assistant that has access to a database containing persona descriptions."
)
# 创建多智能体系统
AgentWorkflow类原生支持多智能体系统,智能体之间可进行任务交接:
from llama_index.core.agent.workflow import (
AgentWorkflow,
FunctionAgent,
ReActAgent,
)
# 定义工具
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers."""
return a + b
def subtract(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Subtract two numbers."""
return a - b
# 创建智能体配置
calculator_agent = ReActAgent(
name="calculator",
description="Performs basic arithmetic operations",
system_prompt="You are a calculator assistant. Use your tools for any math operation.",
tools=[add, subtract],
llm=llm,
)
query_agent = ReActAgent(
name="info_lookup",
description="Looks up information about XYZ",
system_prompt="Use your tool to query a RAG system to answer information about XYZ",
tools=[query_engine_tool],
llm=llm
)
# 创建并运行工作流
agent = AgentWorkflow(
agents=[calculator_agent, query_agent],
root_agent="calculator"
)
# 运行系统
response = await agent.run(user_msg="Can you add 5 and 3?")
6. 在LlamaIndex中创建智能工作流¶
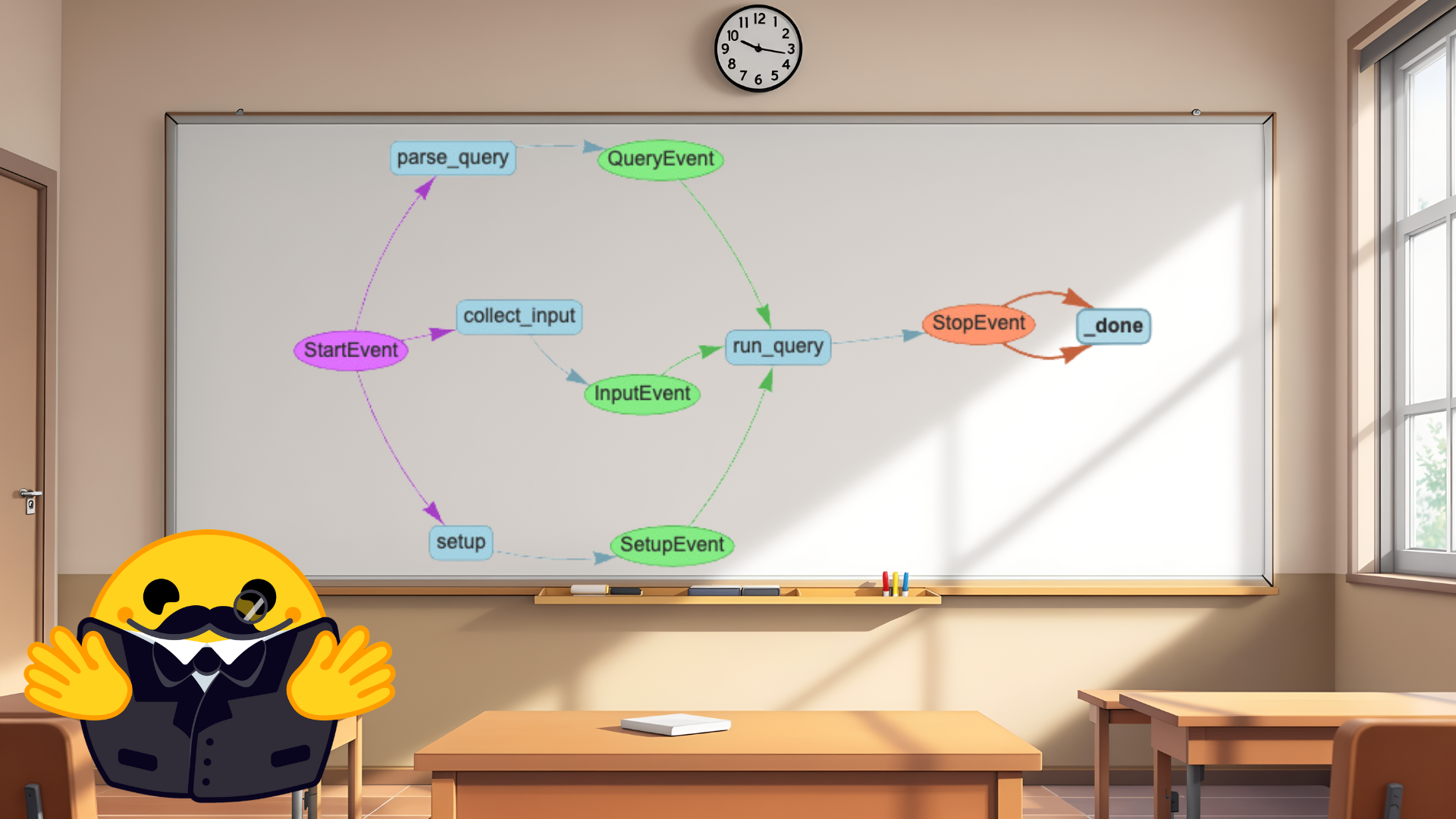
LlamaIndex工作流提供结构化方式组织代码,通过定义由事件(Events)触发的步骤(Steps)创建,步骤本身也会发出事件触发后续步骤。
工作流的关键优势: - 将代码清晰组织为离散步骤 - 事件驱动架构实现灵活控制流 - 步骤间类型安全的通信 - 内置状态管理 - 支持简单和复杂的智能体交互
1. 创建基础工作流
from llama_index.core.workflow import StartEvent, StopEvent, Workflow, step
class MyWorkflow(Workflow):
@step
async def my_step(self, ev: StartEvent) -> StopEvent:
# do something here
return StopEvent(result="Hello, world!")
w = MyWorkflow(timeout=10, verbose=False)
result = await w.run()
2. 连接多个步骤
为连接多个步骤,需创建在步骤之间传输数据的自定义事件:
from llama_index.core.workflow import Event
class ProcessingEvent(Event):
intermediate_result: str
class MultiStepWorkflow(Workflow):
@step
async def step_one(self, ev: StartEvent) -> ProcessingEvent:
# Process initial data
return ProcessingEvent(intermediate_result="Step 1 complete")
@step
async def step_two(self, ev: ProcessingEvent) -> StopEvent:
# Use the intermediate result
final_result = f"Finished processing: {ev.intermediate_result}"
return StopEvent(result=final_result)
w = MultiStepWorkflow(timeout=10, verbose=False)
result = await w.run()
3. 循环和分支
类型提示允许创建分支、循环和连接,促进更复杂的工作流:
from llama_index.core.workflow import Event
import random
class ProcessingEvent(Event):
intermediate_result: str
class LoopEvent(Event):
loop_output: str
class MultiStepWorkflow(Workflow):
@step
async def step_one(self, ev: StartEvent | LoopEvent) -> ProcessingEvent | LoopEvent:
if random.randint(0, 1) == 0:
print("Bad thing happened")
return LoopEvent(loop_output="Back to step one.")
else:
print("Good thing happened")
return ProcessingEvent(intermediate_result="First step complete.")
@step
async def step_two(self, ev: ProcessingEvent) -> StopEvent:
# Use the intermediate result
final_result = f"Finished processing: {ev.intermediate_result}"
return StopEvent(result=final_result)
w = MultiStepWorkflow(verbose=False)
result = await w.run()
4. 绘制工作流程
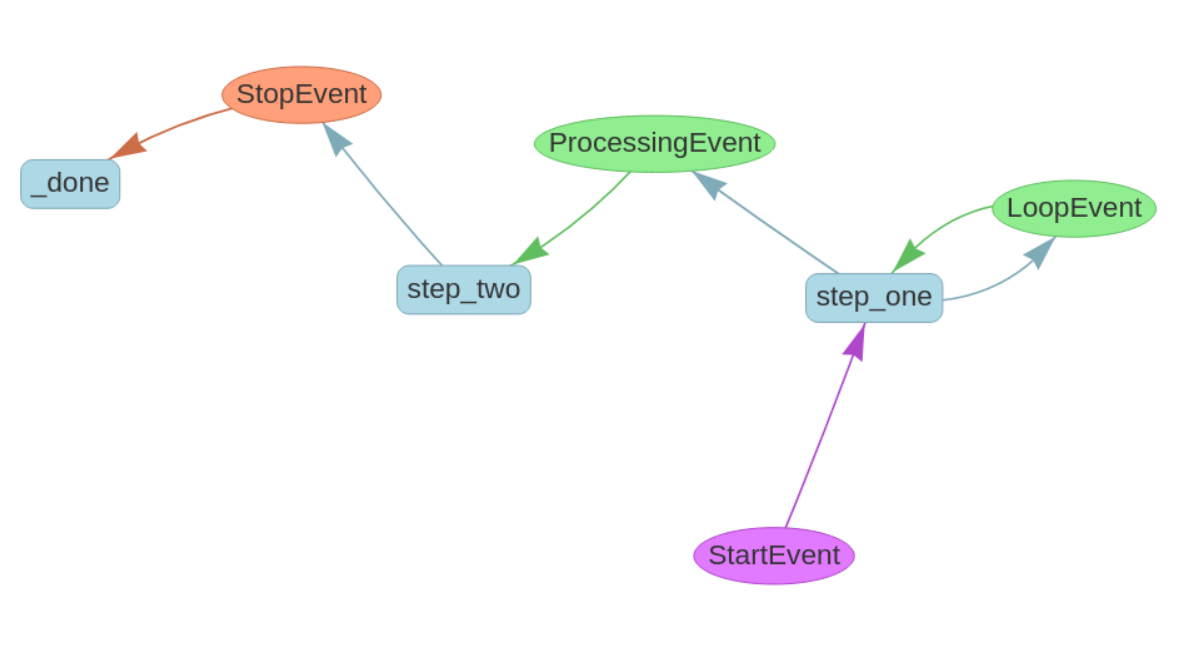
可以使用draw_all_possible_flows函数将工作流可视化:
from llama_index.utils.workflow import draw_all_possible_flows
w = # as defined in the previous section
draw_all_possible_flows(w, "flow.html")
5. 状态管理
当需要跟踪工作流状态时,可以在步骤函数参数上使用"上下文"类型提示:
from llama_index.core.workflow import Context, StartEvent, StopEvent
@step
async def query(self, ctx: Context, ev: StartEvent) -> StopEvent:
# 存储在上下文中
await ctx.set("query", "What is the capital of France?")
# 根据上下文和事件做某事
val = ...
# 从上下文中检索
query = await ctx.get("query")
return StopEvent(result=result)
6. 使用多智能体工作流自动化工作流
AgentWorkflow类可创建多智能体工作流,允许不同智能体协作并相互交接任务:
from llama_index.core.agent.workflow import AgentWorkflow, ReActAgent
from llama_index.llms.huggingface_api import HuggingFaceInferenceAPI
# 定义工具
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers."""
return a + b
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply two numbers."""
return a * b
llm = HuggingFaceInferenceAPI(model_name="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct")
multiply_agent = ReActAgent(
name="multiply_agent",
description="Is able to multiply two integers",
system_prompt="A helpful assistant that can use a tool to multiply numbers.",
tools=[multiply],
llm=llm,
)
addition_agent = ReActAgent(
name="add_agent",
description="Is able to add two integers",
system_prompt="A helpful assistant that can use a tool to add numbers.",
tools=[add],
llm=llm,
)
# 创建工作流
workflow = AgentWorkflow(
agents=[multiply_agent, addition_agent],
root_agent="multiply_agent",
)
# 运行系统
response = await workflow.run(user_msg="Can you add 5 and 3?")
智能体工具还可以修改工作流状态:
from llama_index.core.workflow import Context
# 定义工具
async def add(ctx: Context, a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers."""
# 更新计数
cur_state = await ctx.get("state")
cur_state["num_fn_calls"] += 1
await ctx.set("state", cur_state)
return a + b
async def multiply(ctx: Context, a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Multiply two numbers."""
# 更新计数
cur_state = await ctx.get("state")
cur_state["num_fn_calls"] += 1
await ctx.set("state", cur_state)
return a * b
# 工作流初始化
workflow = AgentWorkflow(
agents=[multiply_agent, addition_agent],
root_agent="multiply_agent",
initial_state={"num_fn_calls": 0},
state_prompt="Current state: {state}. User message: {msg}",
)
# 使用上下文运行工作流
ctx = Context(workflow)
response = await workflow.run(user_msg="Can you add 5 and 3?", ctx=ctx)
# 检查状态
state = await ctx.get("state")
print(state["num_fn_calls"])
7. LlamaIndex 框架完整工作流程图
+--------------------------------+
| 原始数据 |
+---------------+----------------+
|
v
+--------------------------------+
| 数据加载 |
+---------------+----------------+
|
v
+--------------------------------+
| 数据索引 |
+---------------+----------------+
|
v
+--------------------------------+
| 数据存储 |
+---------------+----------------+
|
v
+--------------------------------+
| 查询服务 |
+---------------+----------------+
|
v
+==================================+
| LlamaIndex智能体框架 |
| |
| +-------------+ |
| | 智能体创建 | |
| +------+------+ |
| | |
| v |
| +-------------+ |
| | 工具选择与 | |
| | 配置 | |
| +------+------+ |
| | |
| v |
| +-------------+ |
| | 工作流定义 | |
| +-------------+ |
+==================================+
|
v
+==================================+
| 智能体类型 |
| +-------------+ |
| | 函数调用 | |
| | 智能体 | |
| +-------------+ |
| | ReAct | |
| | 智能体 | |
| +-------------+ |
| | 高级自定义 | |
| | 智能体 | |
| +-------------+ |
+==================================+
|
v
+==================================+
| 工具类型 |
| +-------------+ |
| | FunctionTool| |
| +-------------+ |
| | QueryEngine | |
| | Tool | |
| +-------------+ |
| | Toolspecs | |
| +-------------+ |
| | Utility | |
| | Tools | |
| +-------------+ |
+==================================+
|
v
+==================================+
| 工作流构建 |
| +-------------+ |
| | 事件定义 | |
| +-------------+ |
| | 步骤设计 | |
| +-------------+ |
| | 状态管理 | |
| +-------------+ |
| | 多智能体 | |
| | 协作 | |
| +-------------+ |
+==================================+
|
v
+--------------------------------+
| 完整智能体应用 |
+--------------------------------+
8. 核心概念总结表
| 类别 | 组件 | 主要功能 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 数据处理 | SimpleDirectoryReader | 从本地目录加载文件 | 处理本地多种文件类型 |
| LlamaParse | 官方PDF解析工具 | 处理PDF等复杂文档 | |
| IngestionPipeline | 处理文档转换为节点 | 数据预处理和嵌入 | |
| 索引与存储 | VectorStoreIndex | 创建向量索引 | 语义搜索 |
| ChromaVectorStore | 向量数据存储 | 持久化存储嵌入 | |
| 查询引擎 | QueryEngine | 查询索引生成回答 | 单次问答交互 |
| ChatEngine | 保持对话记忆 | 需要维持上下文的对话 | |
| 工具 | FunctionTool | 包装Python函数 | 执行特定功能 |
| QueryEngineTool | 包装查询引擎 | RAG应用 | |
| Toolspecs | 预设工具集合 | 特定服务集成 | |
| 智能体 | 函数调用智能体 | 直接调用函数 | 支持函数调用的模型 |
| ReAct智能体 | 展示推理过程 | 复杂推理任务 | |
| AgentWorkflow | 多智能体协作 | 复杂系统构建 | |
| 工作流 | Workflow类 | 定义处理步骤 | 结构化任务处理 |
| 事件系统 | 步骤间通信 | 数据传递和流控制 | |
| Context对象 | 状态管理 | 保持工作流状态 |
9. 代码实现主要步骤
- 数据准备:使用SimpleDirectoryReader加载数据,通过IngestionPipeline进行预处理和嵌入
- 索引构建:创建VectorStoreIndex并使用向量存储进行持久化
- 工具定义:构建FunctionTool或QueryEngineTool提供具体功能
- 智能体创建:使用AgentWorkflow配置智能体,赋予其工具调用能力
- 工作流设计:通过事件和步骤设计处理流程,管理状态和智能体交互
- 部署应用:整合以上组件,创建完整的智能体应用
通过这套完整的框架,LlamaIndex提供了从数据处理到智能体协作的全流程支持,使开发者能够构建复杂的智能体应用系统。