UNIT2.1 Smolagents Frameworks¶
smolagents 框架简介¶
1. 什么是 smolagents?
- Hugging Face 开发的一个轻量级 AI 智能体框架
- 它为 LLM 提供了与现实世界互动的能力根
- smolagents 中的 AI 智能体能够基于"观察"生成"思考"并执行"操作"
2. smolagents 的关键优势
| 优势 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 简洁性 | 最小的代码复杂性和抽象层,易于理解、采用和扩展 |
| 灵活的 LLM 支持 | 通过与 Hugging Face 工具和外部 API 的集成,支持任何 LLM |
| 代码优先方法 | 首选支持直接在代码中编写操作的 Code Agents,无需解析并简化工具调用 |
| HF Hub 集成 | 与 Hugging Face Hub 无缝集成,允许使用 Gradio Spaces 作为工具 |
3. 何时使用 smolagents?
smolagents 在以下情况下是理想选择:
- 需要一个轻量级且最小化的解决方案
- 希望快速实验而无需复杂的配置
- 应用逻辑相对简单
4. 代码 vs. JSON 操作
smolagents 与其他框架的主要区别在于智能体操作的表达方式:
- 传统智能体框架:以 JSON 形式编写操作,需要额外的解析步骤
- smolagents:专注于代码中的工具调用,简化了执行过程,直接执行输出
传统方式(JSON):
1. LLM生成JSON格式的工具调用
2. 系统解析JSON
3. 执行对应的工具函数
smolagents方式(Code):
1. LLM直接生成Python代码
2. 系统直接执行代码
5. smolagents 中的智能体类型
smolagents 中的智能体作为多步骤智能体运行。每个 MultiStepAgent 执行:
- 一次思考
- 一次工具调用和执行
支持的主要智能体类型包括:
- CodeAgent:直接生成Python代码(主要类型)
- ToolCallingAgent:以JSON形式编写工具调用
6. smolagents 中的模型集成
smolagents 支持灵活的 LLM 集成,提供多个预定义类以简化模型连接:
| 模型类 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| TransformersModel | 实现本地 transformers 管道 |
| HfApiModel | 支持通过 Hugging Face 基础设施的无服务器推理调用 |
| LiteLLMModel | 利用 LiteLLM 实现轻量级模型交互 |
| OpenAIServerModel | 连接到提供 OpenAI API 接口的任何服务 |
| AzureOpenAIServerModel | 支持与任何 Azure OpenAI 部署集成 |
代码智能体¶
1. 代码智能体概述
代码智能体(Code agents)是smolagents中的默认智能体类型,它们通过生成Python代码来执行操作,而不是生成JSON格式的工具调用。这种方法提供了以下优势:
| 优势 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 可组合性 | 轻松组合和重用操作 |
| 对象管理 | 直接处理复杂结构(如图像) |
| 通用性 | 可以表达任何计算上可能的任务 |
| 适合LLM | 高质量代码已存在于LLM的训练数据中 |
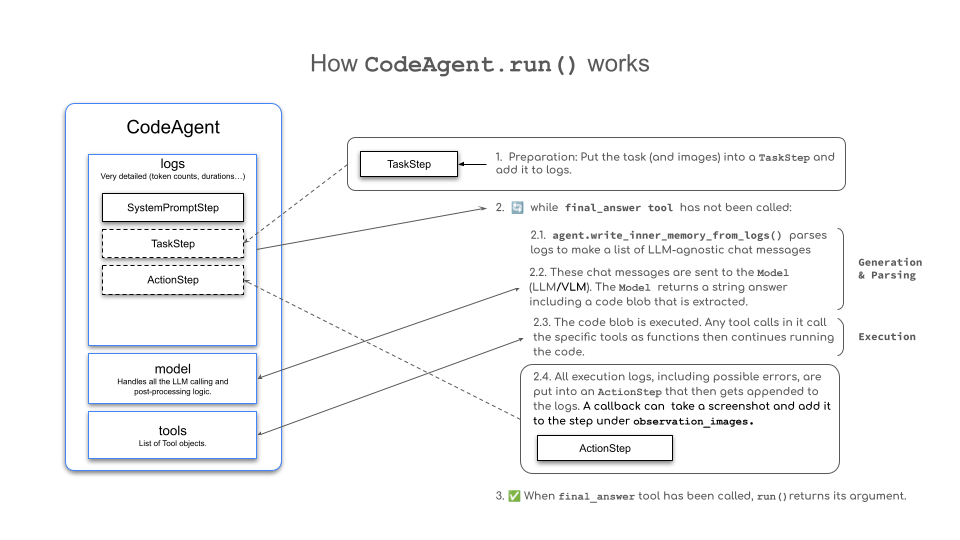
2. CodeAgent工作原理
CodeAgent是smolagents中MultiStepAgent的一种特殊实现,它遵循ReAct框架工作流程:
系统提示 (SystemPromptStep) --> 用户查询 (TaskStep)
|
v
循环过程
|
v
+---------------------------+
| 1. 将智能体日志写入消息列表 |
+---------------------------+
|
v
+---------------------------+
| 2. 发送消息给LLM生成代码 |
+---------------------------+
|
v
+---------------------------+
| 3. 解析并提取代码操作 |
+---------------------------+
|
v
+---------------------------+
| 4. 执行代码并记录结果 |
+---------------------------+
|
v
返回最终结果
代码智能体通过以下步骤执行操作:
- 系统提示存储在
SystemPromptStep中,用户查询记录在TaskStep中 - 智能体执行循环过程:
- 将智能体的日志写入LLM可读的聊天消息列表
- 发送消息给模型生成补全(代码片段)
- 解析补全内容提取代码操作
- 执行代码操作
- 将结果记录到内存中的
ActionStep
3. 实际应用示例
- 为派对选择播放列表
# 安装和导入必要的库
pip install smolagents -U
from smolagents import CodeAgent, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, HfApiModel
from huggingface_hub import login
# 登录到Hugging Face Hub
login()
# 创建带有DuckDuckGo搜索工具的智能体
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], model=HfApiModel())
# 运行智能体搜索派对音乐推荐
agent.run("Search for the best music recommendations for a party at the Wayne's mansion.")
执行过程中,智能体会显示正在执行的代码,例如:
- 使用自定义工具准备菜单
可以通过@tool装饰器创建自定义工具:
from smolagents import CodeAgent, tool
# 根据场合建议菜单的工具
@tool
def suggest_menu(occasion: str) -> str:
"""
Suggests a menu based on the occasion.
Args:
occasion: The type of occasion for the party.
"""
if occasion == "casual":
return "Pizza, snacks, and drinks."
elif occasion == "formal":
return "3-course dinner with wine and dessert."
elif occasion == "superhero":
return "Buffet with high-energy and healthy food."
else:
return "Custom menu for the butler."
# 创建使用菜单工具的智能体
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[suggest_menu], model=HfApiModel())
# 为派对准备正式菜单
agent.run("Prepare a formal menu for the party.")
- 在智能体中使用Python导入
智能体可以使用Python库进行计算,但需要显式授权导入:
from smolagents import CodeAgent, HfApiModel
# 创建允许导入datetime的智能体
agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[],
model=HfApiModel(),
additional_authorized_imports=['datetime']
)
# 请求计算派对准备时间
agent.run("""
Alfred needs to prepare for the party. Here are the tasks:
1. Prepare the drinks - 30 minutes
2. Decorate the mansion - 60 minutes
3. Set up the menu - 45 minutes
3. Prepare the music and playlist - 45 minutes
If we start right now, at what time will the party be ready?
""")
4. 共享智能体到Hub
smolagents允许将创建的智能体共享到Hugging Face Hub,供其他人使用:
# 将智能体推送到Hub
agent.push_to_hub('username/AlfredAgent')
# 从Hub下载智能体
alfred_agent = agent.from_hub('username/AlfredAgent')
alfred_agent.run("Give me the best playlist for a party at Wayne's mansion.")
5. 构建复杂智能体
可以组合多个工具创建功能丰富的智能体:
from smolagents import CodeAgent, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, Tool, tool, VisitWebpageTool, HfApiModel
# 创建菜单推荐工具
@tool
def suggest_menu(occasion: str) -> str:
"""Suggests a menu based on the occasion."""
# 工具实现...
# 创建餐饮服务工具
@tool
def catering_service_tool(query: str) -> str:
"""Returns the highest-rated catering service in Gotham City."""
# 工具实现...
# 创建派对主题工具
class SuperheroPartyThemeTool(Tool):
# 工具定义...
# 创建具有多个工具的派对策划智能体
agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[
DuckDuckGoSearchTool(),
VisitWebpageTool(),
suggest_menu,
catering_service_tool,
SuperheroPartyThemeTool()
],
model=HfApiModel(),
max_steps=10,
verbosity_level=2
)
6. 使用OpenTelemetry和Langfuse监控智能体
smolagents支持使用OpenTelemetry标准检测智能体运行:
# 安装必要依赖
# pip install opentelemetry-sdk opentelemetry-exporter-otlp openinference-instrumentation-smolagents
import os
import base64
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
from openinference.instrumentation.smolagents import SmolagentsInstrumentor
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import SimpleSpanProcessor
# 配置Langfuse API密钥
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY="pk-lf-..."
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY="sk-lf-..."
LANGFUSE_AUTH=base64.b64encode(f"{LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY}:{LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY}".encode()).decode()
# 配置OpenTelemetry
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel"
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS"] = f"Authorization=Basic {LANGFUSE_AUTH}"
# 初始化跟踪器
trace_provider = TracerProvider()
trace_provider.add_span_processor(SimpleSpanProcessor(OTLPSpanExporter()))
SmolagentsInstrumentor().instrument(tracer_provider=trace_provider)
# 现在智能体的运行将被记录到Langfuse
通过这种方式,可以在Langfuse平台上监控和分析智能体的行为,便于调试和优化。
工具调用智能体(ToolCallingAgent)¶
1. 代码智能体 vs 工具调用智能体
smolagents 提供两种主要的智能体类型,它们在操作表达方式上有根本区别:
| 特性 | CodeAgent | ToolCallingAgent |
|---|---|---|
| 操作表达 | Python代码片段 | JSON结构 |
| 执行方式 | 直接执行代码 | 解析JSON后调用工具 |
| 适用场景 | 复杂操作、需要变量处理 | 简单系统、支持工具调用能力的模型 |
| 性能 | 整体表现更好 | 适合简单任务 |
2. 操作表达对比
对于相同任务"搜索餐饮服务和派对创意":
CodeAgent生成:
for query in ["Best catering services in Gotham City", "Party theme ideas for superheroes"]:
print(web_search(f"Search for: {query}"))
ToolCallingAgent生成:
[
{"name": "web_search", "arguments": "Best catering services in Gotham City"},
{"name": "web_search", "arguments": "Party theme ideas for superheroes"}
]
3. 工具调用智能体工作流程
ToolCallingAgent遵循与CodeAgent相同的多步骤工作流,但关键区别在于:
- 生成JSON格式的工具调用指令而非代码
- 系统需要解析JSON并匹配到相应工具
- 执行匹配的工具并返回结果
4. 实现示例
from smolagents import ToolCallingAgent, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, HfApiModel
# 创建工具调用智能体
agent = ToolCallingAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], model=HfApiModel())
# 运行智能体
agent.run("Search for the best music recommendations for a party at the Wayne's mansion.")
执行过程中,您会看到类似以下输出:
╭─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ Calling tool: 'web_search' with arguments: {'query': "best music │
│ recommendations for a party at Wayne's mansion"} │
╰─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
5. 选择指南
- 选择CodeAgent:当需要处理复杂操作、变量管理或多步骤逻辑
- 选择ToolCallingAgent:当使用已内置工具调用能力的模型,或处理简单的单一工具调用场景
工具¶
1. 工具基础概念
工具是智能体系统中LLM可调用的函数,每个工具需要包含以下关键要素:
- 名称:工具的标识符
- 工具描述:工具功能说明
- 输入类型及描述:工具参数说明
- 输出类型:工具返回结果类型
2. 工具创建方法
smolagents提供两种定义工具的方式:
- @tool装饰器(推荐用于简单工具),关键要素:
- 函数名应具有描述性
- 使用类型提示明确输入输出类型
- docstring中详细说明工具功能和参数
from smolagents import tool
@tool
def catering_service_tool(query: str) -> str:
"""
This tool returns the highest-rated catering service in Gotham City.
Args:
query: A search term for finding catering services.
"""
# 示例餐饮服务及评分列表
services = {
"Gotham Catering Co.": 4.9,
"Wayne Manor Catering": 4.8,
"Gotham City Events": 4.7,
}
# 查找评分最高的餐饮服务
best_service = max(services, key=services.get)
return best_service
- Tool类(适用于复杂工具),必需组件:
name:工具名称description:工具描述inputs:输入参数定义output_type:输出类型forward:包含执行逻辑的方法
from smolagents import Tool
class SuperheroPartyThemeTool(Tool):
name = "superhero_party_theme_generator"
description = """
This tool suggests creative superhero-themed party ideas based on a category.
It returns a unique party theme idea."""
inputs = {"category": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The type of superhero party (e.g., 'classic heroes', 'villain masquerade').",
}}
output_type = "string"
def forward(self, category: str):
themes = {
"classic heroes": "Justice League Gala: Guests come dressed as their favorite DC heroes.",
"villain masquerade": "Gotham Rogues' Ball: A mysterious masquerade with Batman villains.",
"futuristic Gotham": "Neo-Gotham Night: A cyberpunk-style party inspired by Batman Beyond."
}
return themes.get(category.lower(), "Themed party idea not found.")
3. 默认工具箱
smolagents提供以下预构建工具:
| 工具名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| PythonInterpreterTool | 执行Python代码 |
| FinalAnswerTool | 提供最终回答 |
| UserInputTool | 获取用户输入 |
| DuckDuckGoSearchTool | 使用DuckDuckGo搜索 |
| GoogleSearchTool | 使用Google搜索 |
| VisitWebpageTool | 访问并解析网页 |
4. 工具共享和导入
- 向Hub共享工具
- 从Hub导入工具
from smolagents import load_tool
# 从Hub加载工具
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image", trust_remote_code=True)
- 将Hugging Face Space作为工具导入
from smolagents import Tool
# 将Space作为工具导入
image_generation_tool = Tool.from_space(
"black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-schnell",
name="image_generator",
description="Generate an image from a prompt"
)
- 导入LangChain工具
from langchain.agents import load_tools
from smolagents import Tool
# 导入LangChain工具
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
5. 工具调用流程
- 智能体接收用户查询
- LLM分析查询并决定调用哪个工具
- 系统使用工具描述生成调用格式
- 工具执行并返回结果
- 结果被整合进智能体的响应
检索智能体(RAG系统)¶
检索增强生成(RAG)系统结合了数据检索和生成模型的能力,提供上下文感知的响应。smolagents支持构建智能驱动的RAG系统,与传统RAG相比有以下优势:
| 传统RAG | 智能驱动RAG |
|---|---|
| 依赖单次检索步骤 | 允许多次迭代检索 |
| 关注与查询的直接语义相似性 | 智能制定搜索查询和评估结果 |
| 固定检索流程 | 自主控制检索和生成过程 |
1. 实现检索智能体的两种方式
- 基于网络搜索的检索
from smolagents import CodeAgent, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, HfApiModel
agent = CodeAgent(
model=HfApiModel(),
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()]
)
response = agent.run("Search for luxury superhero-themed party ideas")
- 自定义知识库检索
from langchain.docstore.document import Document
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.retrievers import BM25Retriever
from smolagents import Tool, CodeAgent, HfApiModel
class PartyPlanningRetrieverTool(Tool):
name = "party_planning_retriever"
description = "Retrieves party planning ideas"
inputs = {"query": {"type": "string", "description": "The search query"}}
output_type = "string"
def __init__(self, docs, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.retriever = BM25Retriever.from_documents(docs, k=5)
def forward(self, query: str) -> str:
docs = self.retriever.invoke(query)
return "\n".join([f"===== Idea {i} =====\n{doc.page_content}"
for i, doc in enumerate(docs)])
2. 高级检索策略
- 查询重构:优化原始查询以匹配目标文档
- 多步检索:利用初步结果优化后续查询
- 多源整合:结合网页搜索和本地文档等多个来源
- 结果验证:在纳入响应前分析内容相关性和准确性
多智能体系统¶
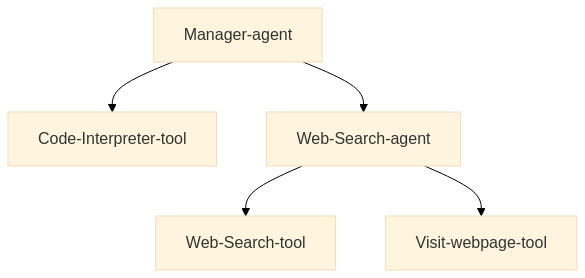
多智能体系统允许专业智能体在复杂任务上协作,提高模块化、可扩展性和稳健性。常见的架构包括:
+----------------+
| 管理智能体 |
| (Orchestrator) |
+--------+-------+
|
v
+--------+---------+ +--------------+ +-------------+
| 网络搜索智能体 | <-> | 代码解释智能体 | <-> | 检索智能体 |
+------------------+ +--------------+ +-------------+
实现多智能体系统示例:
# 创建专门的网络搜索智能体
web_agent = CodeAgent(
model=HfApiModel(),
tools=[GoogleSearchTool(), VisitWebpageTool()],
name="web_agent",
description="Browses the web to find information"
)
# 创建管理智能体
manager_agent = CodeAgent(
model=HfApiModel(),
tools=[calculate_travel_time], # 自定义工具
managed_agents=[web_agent], # 管理的子智能体
additional_authorized_imports=["pandas", "plotly"],
planning_interval=5, # 每5步进行规划
)
# 可视化智能体结构
manager_agent.visualize()
# 执行复杂任务
manager_agent.run("""
Find all Batman filming locations in the world, calculate the time to transfer via cargo plane,
and represent this as spatial map with color based on travel time.
""")
通过在两个智能体间分割任务,可以实现:
- 每个智能体更专注于核心任务,提高性能
- 分离记忆减少每步输入令牌数,降低延迟和成本
- 更好地处理复杂、多阶段任务
视觉和浏览器智能体¶
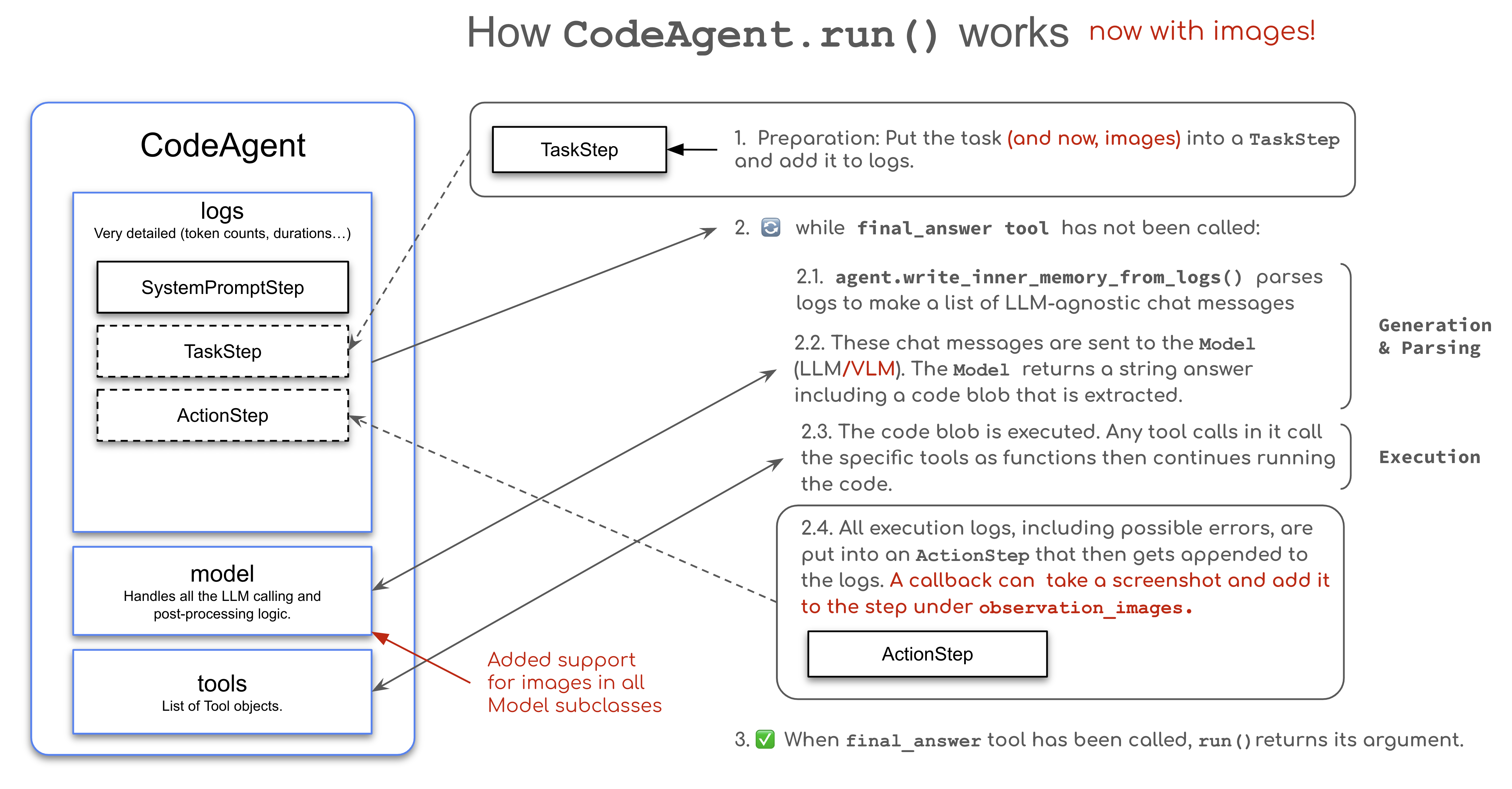
1. 视觉智能体
视觉智能体能够处理和解释图像信息,对于网页浏览、文档理解等任务至关重要。smolagents支持两种方式处理图像:
- 初始执行阶段提供图像
from PIL import Image
import requests
from io import BytesIO
from smolagents import CodeAgent, OpenAIServerModel
# 获取图像
image_urls = ["https://example.com/image1.jpg", "https://example.com/image2.jpg"]
images = []
for url in image_urls:
response = requests.get(url)
image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
images.append(image)
# 创建视觉智能体
agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[],
model=OpenAIServerModel(model_id="gpt-4o"),
max_steps=20
)
# 在启动时传入图像
response = agent.run("Describe the character in these photos", images=images)
2. 动态检索图像(如网页浏览)
浏览器智能体通过动态获取屏幕截图,可以解析网页内容、识别界面元素,并根据视觉信息做出决策:
from smolagents import CodeAgent, OpenAIServerModel, DuckDuckGoSearchTool
# 创建截图回调函数
def save_screenshot(step_log, agent):
driver = helium.get_driver()
if driver is not None:
png_bytes = driver.get_screenshot_as_png()
image = Image.open(BytesIO(png_bytes))
step_log.observations_images = [image.copy()]
# 创建带浏览器工具的视觉智能体
agent = CodeAgent(
tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool(), go_back, close_popups, search_item_ctrl_f],
model=OpenAIServerModel(model_id="gpt-4o"),
additional_authorized_imports=["helium"],
step_callbacks=[save_screenshot] # 每步保存截图
)
# 执行需要视觉理解的浏览任务
agent.run("""
Search for images of Wonder Woman and generate a detailed visual description
based on those images. Navigate to Wikipedia to gather key details about her appearance.
""")