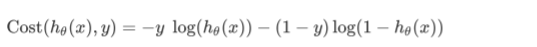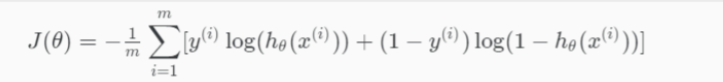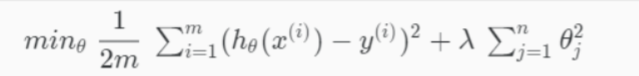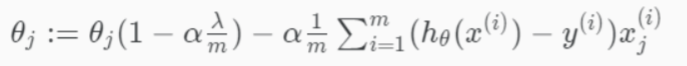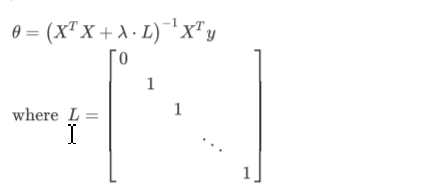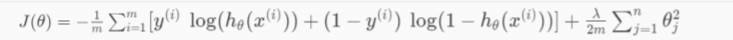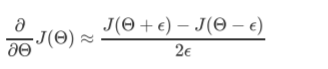MachineLearning(AndrewNg)Notes-Week1-Week5总结
Liner Regression
-
Cost Function
$h(x)=\theta_0+\theta_1x+….$
$h(x)=\theta^Tx$
-
Linear Regression
$J(\theta) = \frac{1}{2m}\sum_{1}^{m}(h_\theta(x^i)-y^i)$
$\frac{\partial{J(\theta)}}{\partial{\theta_j}}=\frac{1}{m}\sum_{1}^{m}(h_\theta(x^i)-y^i)$
-
Gradient descent algorithm
repeat until convergence{
$\theta_j := \theta_j - \frac{ \alpha}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}(h_\theta(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)}) x^{(i)}$
}
-
Feature scaling and mean normalization
$x_i=\frac{x_i-\mu_i}{s_i}$
$\mu_i$: the average of all the values for feature (i)
$s_i$ : standard deviation
-
learning rate
If α is too small: slow convergence. If α is too large: may not decrease on every iteration and thus may not converge.
-
Polynomial Regression
change the behavior or curve of our hypothesis function by making it a quadratic, cubic or square root function (or any other form).
-
Normal Equation
$\theta = (X^TX)^{-1}X^Ty$
-
Logistic Regression
-
Logistic Function or Sigmoid Function

-
Decision Boundary
$\theta^Tx \ge 0 \Rightarrow y=1$
$\theta^Tx \le 0 \Rightarrow y=0$
-
Cost Function

-
Gradient Descent

-
$h=g(X\theta)$
$J(\theta)=\frac{1}{m}(-y’log(h)-(1-y)’log(1-h))$
-
$\theta:=\theta-\frac{\alpha}{m}X^T(g(\theta X) -y)$
-
-
Advanced Optimization
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8function [jVal, gradient] = costFunction(theta) jVal = [...code to compute J(theta)...]; gradient = [...code to compute derivative of J(theta)...]; end options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 100); initialTheta = zeros(2,1); [optTheta, functionVal, exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction, initialTheta, options); -
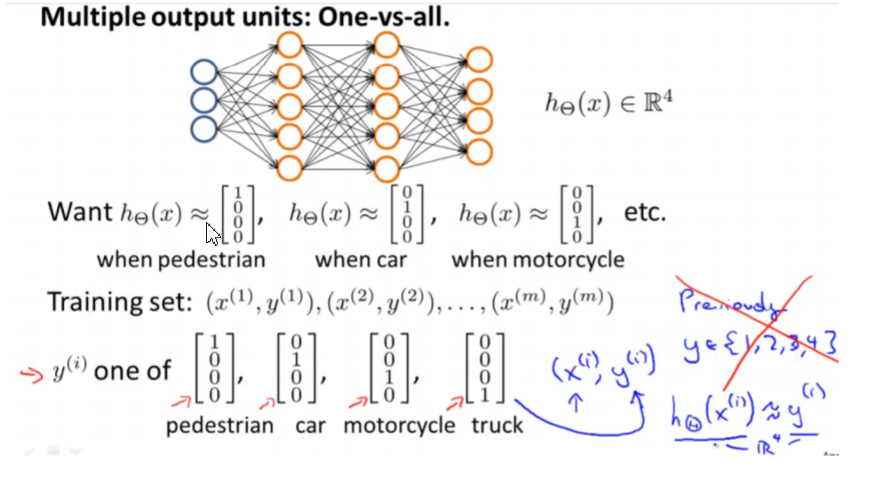
Multiclass Classification: One-vs-all
Train a logistic regression classifier $h_\theta(X)$ for each class to predict the probability that y = i . To make a prediction on a new x, pick the class that maximizes $h_\theta(X)$
-
Overfitting
-
Reduce the number of features
-
Regularization



-
-
Regularized Logistic Regression

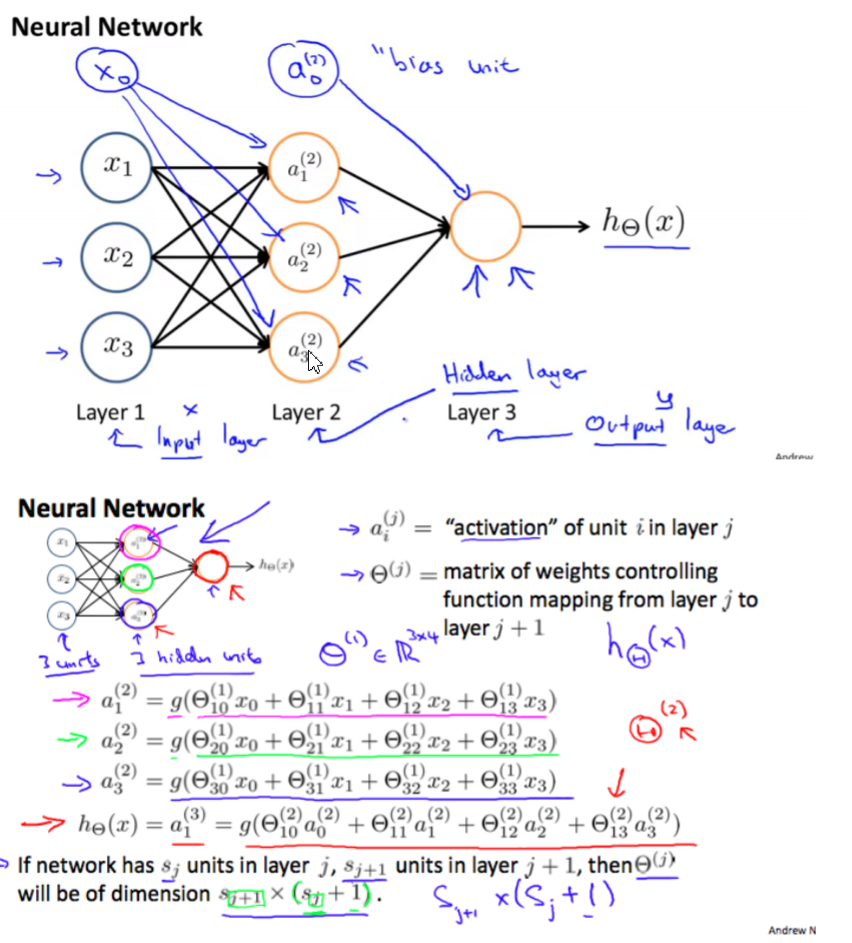
Neural Networks
-
Model Representation
- Forward propagation:Vectorized implementation

-
Multiclass Classification
one-vs-all

-
Neural Network(Classification)
L = total number of layers in the network $s_l$= number of units (not counting bias unit) in layer l K = number of output units/classes
-
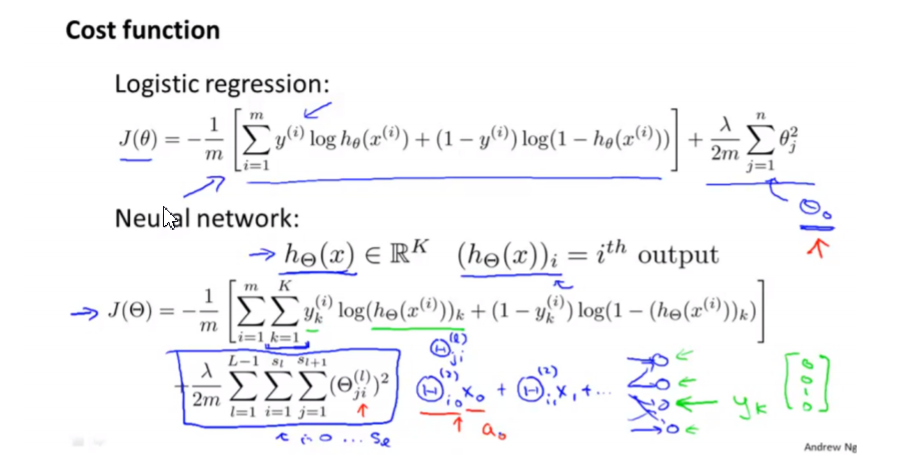
Cost Function

-
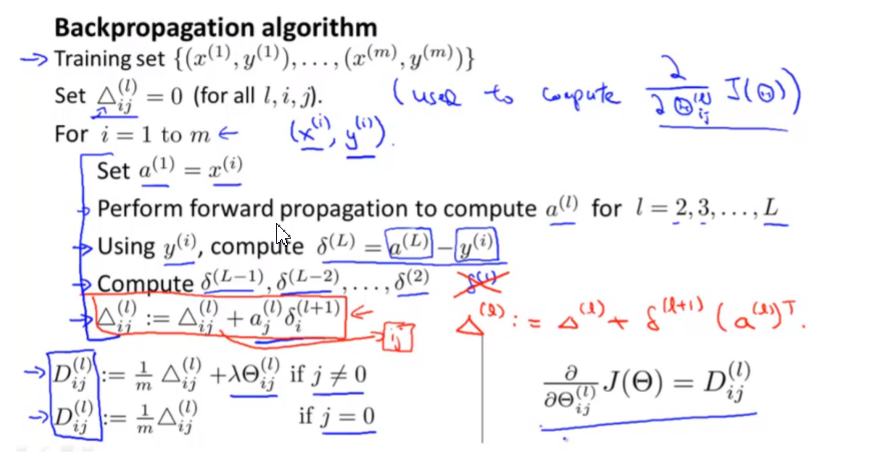
Backpropagation Algorithm

-
Gradient Checking

-
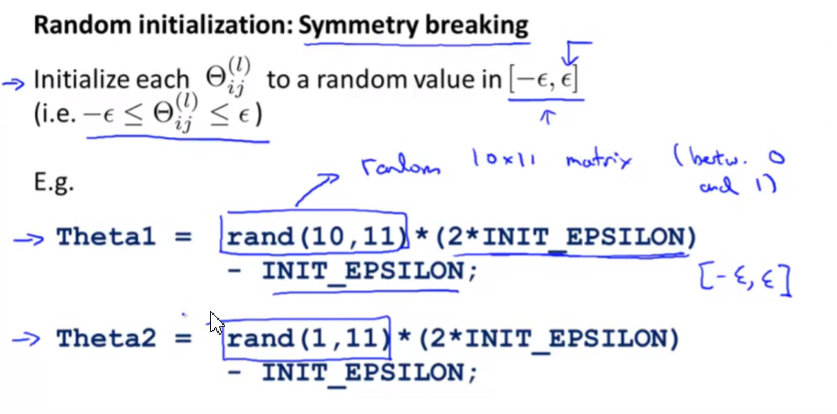
Random Initialization

-