Lab: Xv6 and Unix utilities¶
https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.1810/2023/labs/util.html
0. MacOs Environments¶
For this class we'll need the RISC-V versions of a couple different tools: QEMU 5.1+, GDB 8.3+, GCC, and Binutils.
Previously installed corresponding programs can be omitted by yourself.
- First, install developer tools:
- Next, install Homebrew, a package manager for macOS:
$ /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
- Next, install the RISC-V compiler toolchain:
- The brew formula may not link into /usr/local. You will need to update your shell's rc file (e.g. ~/.bashrc) to add the appropriate directory to $PATH.
- Finally, install QEMU:
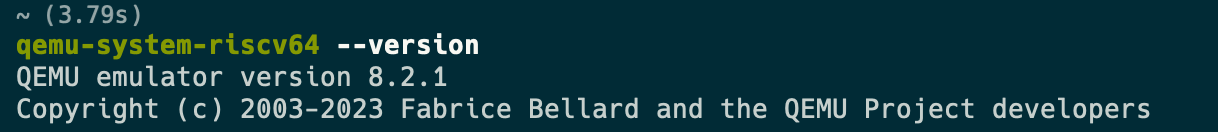
- Testing your Installation:
$ qemu-system-riscv64 --version
QEMU emulator version 5.1.0
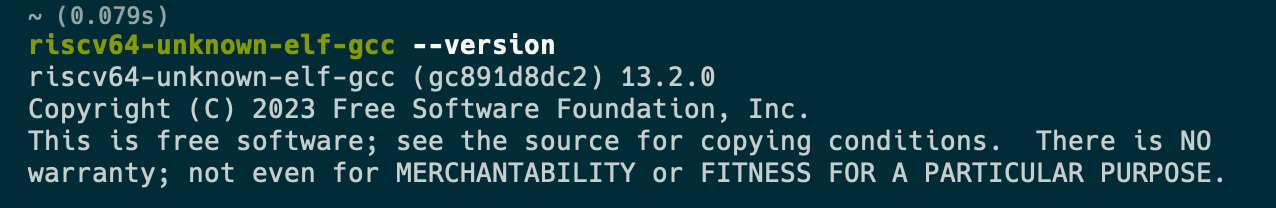
$ riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc --version
riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc (GCC) 10.1.0
...
1. Boot xv6¶
- Fetch the git repository for the xv6 source for the lab:
$ git clone git://g.csail.mit.edu/xv6-labs-2023
Cloning into 'xv6-labs-2023'...
...
$ cd xv6-labs-2023
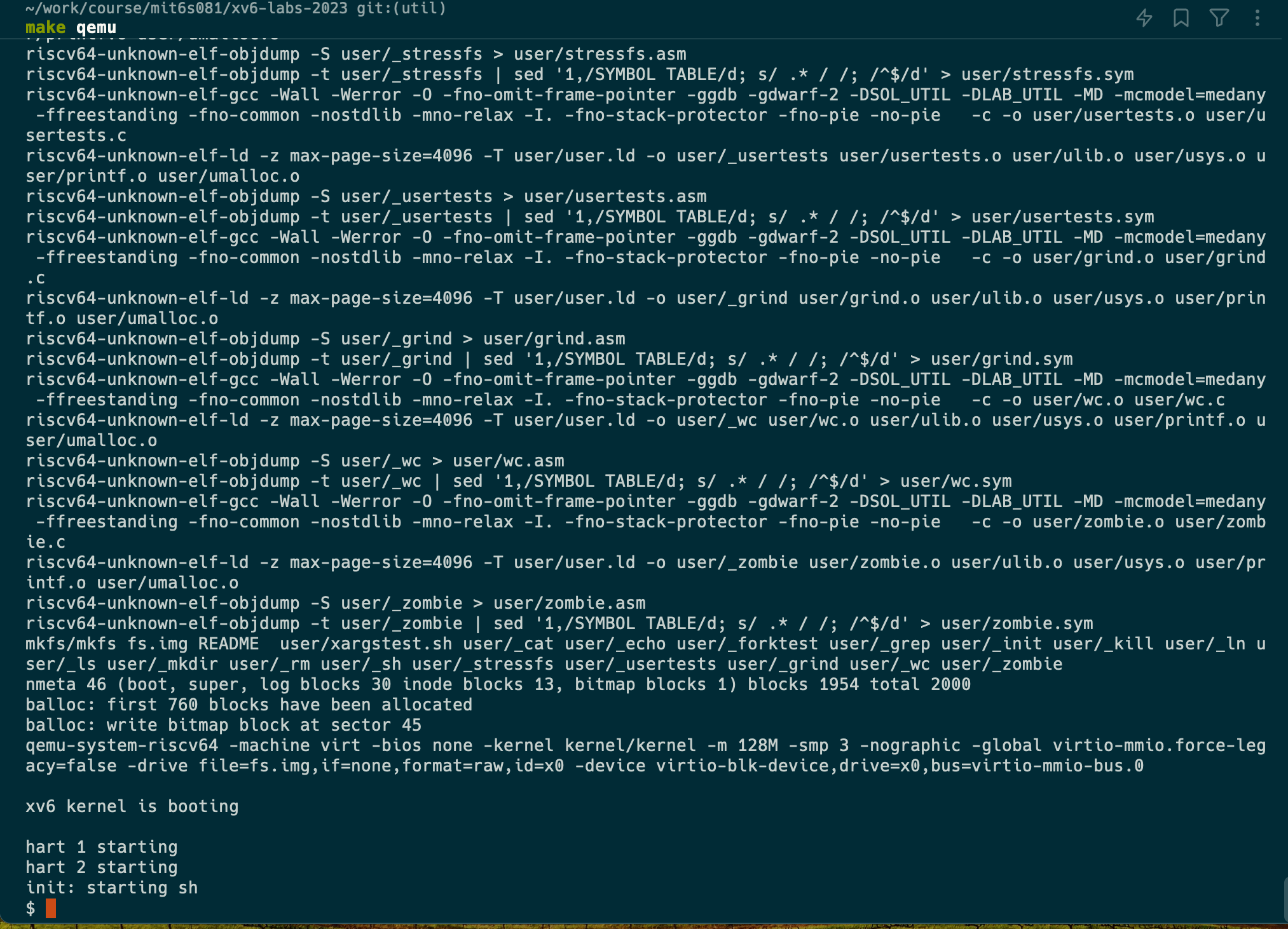
- Build and run xv6:
$ make qemu
riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc -c -o kernel/entry.o kernel/entry.S
riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc -Wall -Werror -O -fno-omit-frame-pointer -ggdb -DSOL_UTIL -MD -mcmodel=medany -ffreestanding -fno-common -nostdlib -mno-relax -I. -fno-stack-protector -fno-pie -no-pie -c -o kernel/start.o kernel/start.c
...
riscv64-unknown-elf-ld -z max-page-size=4096 -N -e main -Ttext 0 -o user/_zombie user/zombie.o user/ulib.o user/usys.o user/printf.o user/umalloc.o
riscv64-unknown-elf-objdump -S user/_zombie > user/zombie.asm
riscv64-unknown-elf-objdump -t user/_zombie | sed '1,/SYMBOL TABLE/d; s/ .* / /; /^$/d' > user/zombie.sym
mkfs/mkfs fs.img README user/xargstest.sh user/_cat user/_echo user/_forktest user/_grep user/_init user/_kill user/_ln user/_ls user/_mkdir user/_rm user/_sh user/_stressfs user/_usertests user/_grind user/_wc user/_zombie
nmeta 46 (boot, super, log blocks 30 inode blocks 13, bitmap blocks 1) blocks 954 total 1000
balloc: first 591 blocks have been allocated
balloc: write bitmap block at sector 45
qemu-system-riscv64 -machine virt -bios none -kernel kernel/kernel -m 128M -smp 3 -nographic -drive file=fs.img,if=none,format=raw,id=x0 -device virtio-blk-device,drive=x0,bus=virtio-mmio-bus.0
xv6 kernel is booting
hart 2 starting
hart 1 starting
init: starting sh
- xv6 has no ps command, but, if you type
Ctrl-p, the kernel will print information about each process.- If you try it now, you'll see two lines: one for init, and one for
sh.
- If you try it now, you'll see two lines: one for init, and one for
- To quit qemu type:
Ctrl-a x(pressCtrlandaat the same time, followed by x).
2. sleep(easy)¶
Implement a user-level sleep program for xv6, along the lines of the UNIX sleep command. Your sleep should pause for a user-specified number of ticks. A tick is a notion of time defined by the xv6 kernel, namely the time between two interrupts from the timer chip. Your solution should be in the file user/sleep.c.
即实现系统函数 sleep 的功能,根据提示进行实现,其中关键点就是:
- 当用户参数缺失时,需要提示错误信息
- 系统函数 sleep 的入参是整型,而在终端获取的值是字符,此时可使用 atoi 函数
具体代码如下:
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "user/user.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(2, "usage: sleep [ticks num]\n");
exit(1);
}
int ticks = atoi(argv[1]);
int ret = sleep(ticks);
exit(ret);
}
3. pingpong(easy)¶

该题主要考查 pipe、fork 的使用和文件描述符的读写应用。根据提示和参考示例8进行实现,其中较为关键的是:
- 父子进程是双向通信,ping 和 pong 需要两个 pipe
- 为了避免资源泄漏和阻塞,可通过 close 关闭不再需要的 pipe 端口
- 在 read pipe 时是进程阻塞的,直到有数据 write pipe 后才会继续向下执行
具体代码如下:
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "user/user.h"
int main(){
int pid,fork_pid;
int child_pipe[2],parent_pipe[2];
char buf[] = {'a'};
pipe(child_pipe);
pipe(parent_pipe);
fork_pid = fork();
if (fork_pid == 0) { // child
pid = getpid();
// step2: read a byte from the parent, and print
close(parent_pipe[1]);
read(parent_pipe[0],buf,1);
printf("%d: received ping\n",pid);
// step3: write a byte to the parent
close(child_pipe[0]);
write(child_pipe[1],buf,1);
} else { // parent
pid = getpid();
// step1: send a byte to the child
close(parent_pipe[0]);
write(parent_pipe[1],buf,1);
// step4: read a byte from the child, and print
close(child_pipe[1]);
read(child_pipe[0],buf,1);
printf("%d: received pong\n",pid);
}
exit(0);
}
4. primes(moderate/hard)¶

即实现Sieve质数算法,在 https://swtch.com/~rsc/thread/ 中实际上提示了关键思路:
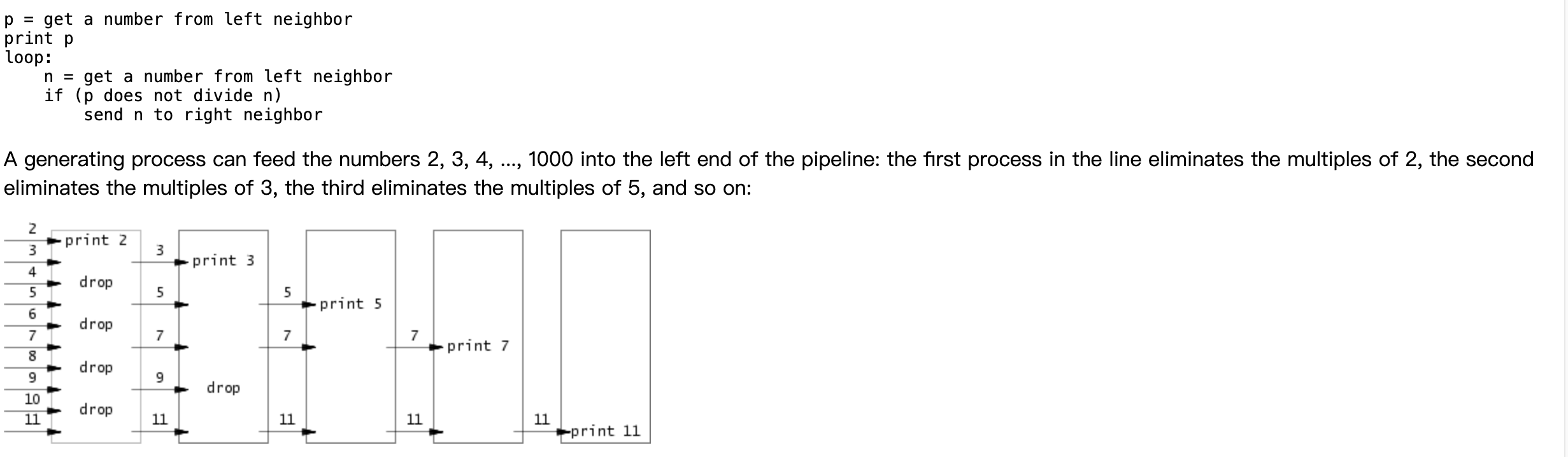
根据上述思路,通过 pipe 和 fork 进行实现,其中还需要特别注意:
- 为了保证进程生命周期链的正确性,需要等待所有子进程都结束,则需要将 fork 出来的子进程进行 wait
- 为了避免超过 xv6 系统的 fd 上限,需要及时关闭不再使用的文件描述符,这样也能减少进程被卡住的概率
具体代码如下:
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "user/user.h"
__attribute__((noreturn))
void deliver_process(int read_fd){
int cur_num = 0;
int is_fork = 0;
int pass_num = 0;
int pipes[2];
while(1){
// get a number from the left neighbor
int read_len = read(read_fd,&pass_num,4);
// the left neighbor empty or close
if (read_len == 0 ){
close(read_fd);
if (is_fork){
close(pipes[1]);
close(pipes[0]);
wait(0);
}
exit(0);
}
if (cur_num==0){
cur_num = pass_num;
printf("prime %d\n",cur_num);
}
if (pass_num%cur_num!=0) {
if (!is_fork){
// create new process and pipe
pipe(pipes);
is_fork = 1;
int pid = fork();
if (pid==0){ // child
// next process handle
// deliver to the next process pipes for writing
close(pipes[1]);
close(read_fd);
deliver_process(pipes[0]);
} else{ // parent
close(pipes[0]);
}
}
// send n to the right neighbor
write(pipes[1],&pass_num,4);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int pipes[2];
pipe(pipes);
for (int i=2;i<=35;i++) {
write(pipes[1],&i,4);
}
close(pipes[1]);
deliver_process(pipes[0]);
exit(0);
}
5. find(moderate)¶

此系统命令的功能为:
- 输入:一个初始路径和一个目标文件名
- 输出:递归扫描该初始路径下的所有目录,匹配与文件名相同的文件并输出
根据提示中提到的 user/ls.c,来了解读取目录信息的实现,这里给出关键代码的注释:
void
ls(char *path)
{
char buf[512], *p;
int fd;
struct dirent de;
struct stat st;
// 通过 open 函数获取特定路径的文件描述符
if((fd = open(path, O_RDONLY)) < 0){
fprintf(2, "ls: cannot open %s\n", path);
return;
}
// 通过 fstat 函数获取该文件描述符的详细信息
if(fstat(fd, &st) < 0){
fprintf(2, "ls: cannot stat %s\n", path);
close(fd);
return;
}
// 通过 st.type 来识别当前文件描述符的类型信息(设备、文件、目录)
// 这里主要关注目录的处理
switch(st.type){
case T_DEVICE:
case T_FILE:
printf("%s %d %d %l\n", fmtname(path), st.type, st.ino, st.size);
break;
case T_DIR:
// 目录的长度避免超过 xv6 设置的缓冲区上限
// DIRSIZ 被用于计算路径名的长度,以确保不会超出缓冲区的大小
if(strlen(path) + 1 + DIRSIZ + 1 > sizeof buf){
printf("ls: path too long\n");
break;
}
// 将 path 字符串复制到 buf 中
strcpy(buf, path);
// 遍历当前目录信息的关键代码
// 变量 p 即表示路径的字符串指针
p = buf+strlen(buf);
*p++ = '/';
while(read(fd, &de, sizeof(de)) == sizeof(de)){
if(de.inum == 0)
continue;
// memmove 函数即表示从源内存区域复制 n 个字节到目标内存区域
// 每次遍历需要赋值其文件名称的完整路径(即 path+file)
memmove(p, de.name, DIRSIZ);
p[DIRSIZ] = 0;
if(stat(buf, &st) < 0){
printf("ls: cannot stat %s\n", buf);
continue;
}
printf("%s %d %d %d\n", fmtname(buf), st.type, st.ino, st.size);
}
break;
}
// 最后使用完后需要关闭文件描述符
close(fd);
}
在上面处理的基础上,我们还需要在过程中不断递归子目录,直至匹配到文件名相同的文件后进行输出,其中还需要注意:
- 不要递归
.和.. - 在匹配文件名称的字符串时,需要使用 strcmp 函数
具体代码如下:
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "user/user.h"
#include "kernel/fs.h"
#include "kernel/fcntl.h"
// get the filename from the whole path
char* get_filename(char *path){
char *p;
// Find first character after last slash.
for(p=path+strlen(path);p>=path&&*p!='/';p--)
;
p++;
return p;
}
void find(char *path,char *target){
char buf[512],*p;
int fd;
struct dirent de;
struct stat st;
if((fd = open(path, O_RDONLY)) < 0){
fprintf(2, "find: cannot open %s\n", path);
return;
}
if(fstat(fd,&st)<0){
fprintf(2, "find: cannot stat %s\n", path);
close(fd);
return;
}
switch(st.type){
case T_DEVICE:
case T_FILE:
// 检查是否匹配目标文件名称
char *f_name= get_filename(path);
// printf("filename:%s,target:%s\n",f_name,target);
if (strlen(f_name) != 0 && strcmp(f_name,target) == 0){
printf("%s\n",path);
}
close(fd);
break;
case T_DIR:
if(strlen(path) + 1 + DIRSIZ + 1 > sizeof buf){
printf("find: path too long\n");
break;
}
strcpy(buf, path);
p = buf+strlen(buf);
*p++ = '/';
while(read(fd,&de,sizeof(de)) == sizeof(de)){
if(de.inum==0||strcmp(de.name,".")==0||strcmp(de.name,"..")==0){
continue;
}
memmove(p, de.name, DIRSIZ);
p[DIRSIZ] = 0;
if(stat(buf, &st) < 0){
printf("find: cannot stat %s\n", buf);
continue;
}
// printf("p:%s,buf:%s\n",p,buf);
find(buf, target);
}
close(fd);
break;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
if(argc != 3){
fprintf(2,"find usage: find [dir] [filename]\n");
exit(1);
}
find(argv[1],argv[2]);
exit(0);
}
6. xargs(moderate)¶

这里需要实现的功能为:
- 参数描述要运行的命令,它从标准输入读取行,并为每一行运行命令,并将该行附加到命令的参数中
结合提示信息,该命令实现的核心处理有以下几点:
- 通过读取文件描述符的值为 0 来判断输入结束
- 使用
fork和exec在每行输入上调用命令,且注意在父级中使用wait等待子级完成命令 - 若想要读取单行输入,则可遍历读取单个字符,直至出现换行符即
\n,在实际实现过程中还需要通过 buf 来截取处理
具体代码如下:
#include "kernel/param.h"
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "user/user.h"
#define buf_size 512
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char buf[buf_size+1] = {0};
char *xargv[MAXARG] = {0};
int used_size = 0;
int stdin_end = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
xargv[i - 1] = argv[i];
}
while (!stdin_end || used_size != 0) {
if (!stdin_end) {
int read_bytes = read(0, buf + used_size, buf_size - used_size);
if (read_bytes < 0) {
fprintf(2, "xargs: read returns -1 error\n");
exit(1);
}
if (read_bytes == 0) {
close(0);
stdin_end = 1;
}
used_size += read_bytes;
}
char *line_end = strchr(buf, '\n');
while (line_end) {
char xbuf[buf_size + 1] = {0};
memcpy(xbuf, buf, line_end - buf);
xargv[argc - 1] = xbuf;
int pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) { // child
if (!stdin_end) {
close(0);
}
if (exec(argv[1], xargv) < 0) {
fprintf(2, "xargs: exec fails with -1\n");
exit(1);
}
} else { // parent
int remain_line = line_end - buf;
memmove(buf, line_end + 1, used_size - remain_line - 1);
used_size -= remain_line + 1;
memset(buf + used_size, 0, buf_size - used_size);
wait(0);
}
line_end = strchr(buf, '\n');
}
}
exit(0);
}